In the evolving world of medical technology, Biocompatible Polymers stand out as game-changers, offering unparalleled safety and functionality in medical applications. These advanced materials, including specialized forms like diblock copolymers, are engineered to interact seamlessly with biological systems, making them essential for a variety of healthcare solutions. From medical implants and drug delivery systems to tissue engineering and wound care, biocompatible polymers play a crucial role in enhancing patient outcomes and advancing medical innovations.
Biocompatible polymers are made to be compatible with living tissues and fluids, ensuring that they do not provoke adverse reactions when introduced into the body. This unique characteristic makes them ideal for use in applications where interaction with biological systems is necessary.
By minimizing the risk of toxicity, inflammation, or rejection, these polymers contribute significantly to the development of safe and effective medical devices. Whether you're exploring options for medical implants, designing controlled drug delivery systems, or developing new tissue engineering solutions, understanding the properties and applications of biocompatible polymers. With their ability to integrate harmoniously with the body, these materials are paving the way for innovations that improve health and quality of life.
Biocompatible polymers are materials made to be compatible with living tissues and biological systems. Unlike traditional polymers, these materials are engineered to minimize adverse reactions when used in medical applications. Key characteristics of biocompatible polymers include non-toxicity, biodegradability, mechanical strength, and controlled interaction with biological systems.
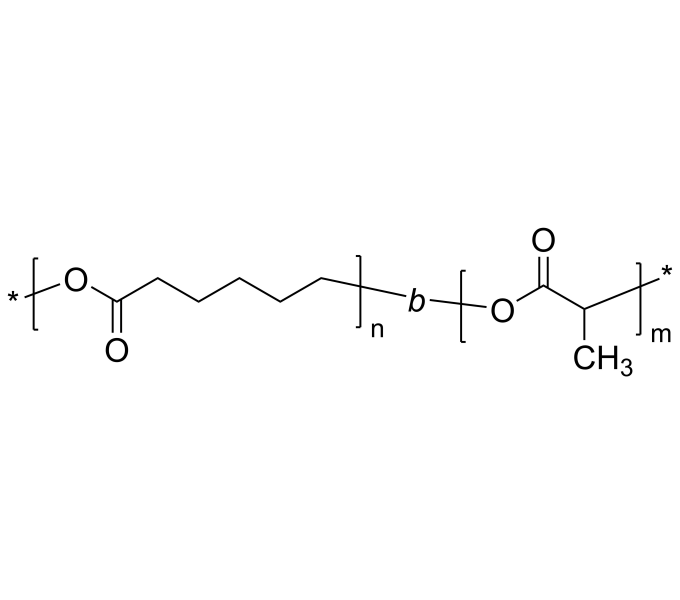


Biocompatible polymer suppliers play a crucial role in the medical and biotechnology industries. They provide the high-quality materials needed for various applications, from implants and drug delivery systems to wound dressings and tissue engineering. Choosing a reliable supplier ensures that the biocompatible polymers, including diblock copolymers, meet stringent safety and performance standards, which is vital for successful medical outcomes.
Biocompatible polymers are essential for developing innovative medical technologies. They ensure that materials used in medical devices and treatments are safe, effective, and well-tolerated by the body. The ongoing research and advancements in biocompatible polymers, continue to shape the future of medicine, enhancing patient care and improving health outcomes.
Biocompatible polymers are a cornerstone of modern medical technology, offering safe and effective solutions across a range of applications. From medical implants and drug delivery systems to tissue engineering and wound care, these polymers are integral to advancing healthcare. The role of Biocompatible Polymer Suppliers is crucial in ensuring that these materials meet high standards of quality and safety, paving the way for future medical innovations.
As a leading global provider of polymer analysis services, we maintain a strong network of distributors across key regions, including the USA, China, the UK, Japan, Australia, Singapore, Canada, and more.
Contact us today to learn how our high-quality polymer solutions can advance your research and development projects. Our dedicated team is ready to help you achieve your project goals and drive innovation.